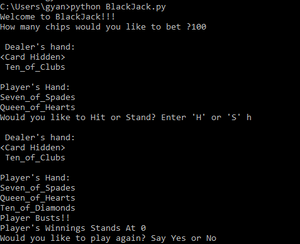
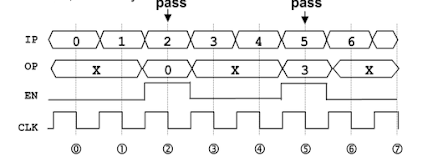
Problem : Design a digital circuit as depicted in below block diagram which takes DIN as an input and runs at a clock speed of CLK and generates an output DATA as shown in the waveform below.Solution : - Since the circuit sample the data at both positive and negative edge of the clock, we need both...